Overview
Aortic valve stenosis
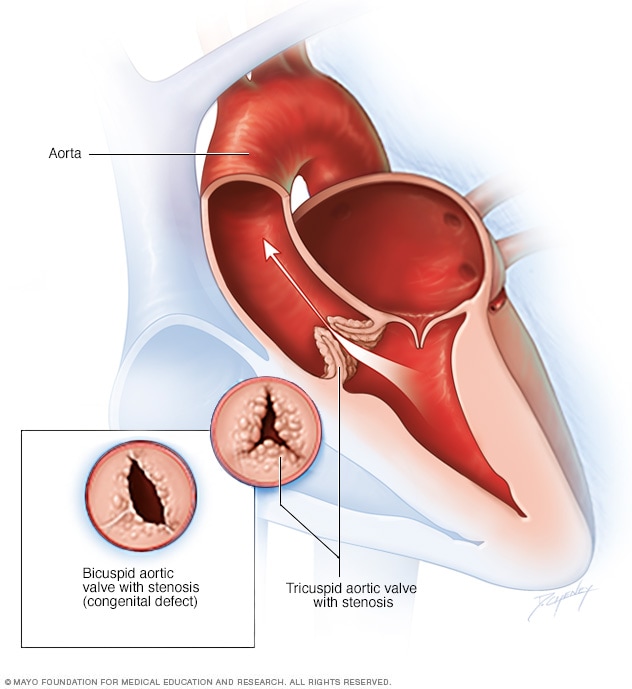
Aortic valve stenosis
Aortic valve stenosis causes a thickening and narrowing of the valve between the heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle) and the body's main artery (aorta). The narrowing creates a smaller opening for blood to pass through. Blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body is reduced or blocked. Typically, the aortic valve has three cusps (tricuspid aortic valve), but some people are born with an aortic valve that has two cusps (bicuspid aortic valve).
Aortic valve regurgitation
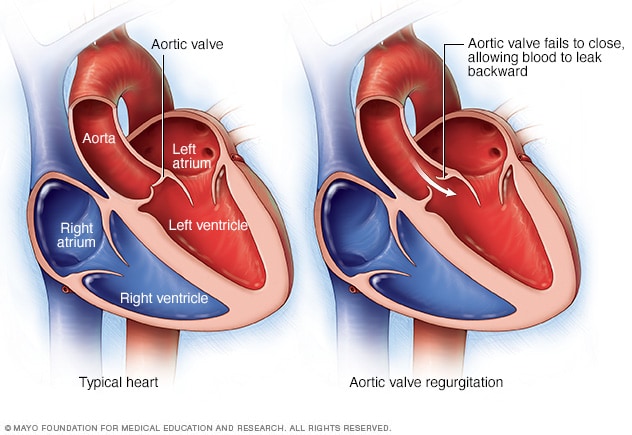
Aortic valve regurgitation
In aortic valve regurgitation, the aortic valve doesn't close properly, causing blood to flow backward from the body's main artery (aorta) into the lower left heart chamber (left ventricle).
Aortic valve disease is a type of heart valve disease. In aortic valve disease, the valve between the lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) and the main artery to the body (aorta) doesn't work properly.
The aortic valve helps keep blood flowing in the correct direction through the heart. A damaged or diseased aortic valve can affect blood flow to the rest of the heart and body.
Aortic valve disease includes:
- Aortic valve stenosis. The flaps (cusps) of the aortic valve become thick and stiff, or they fuse together. These problems cause the valve opening to become narrow. The narrowed valve reduces or blocks blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
- Aortic valve regurgitation. The aortic valve doesn't close properly, causing blood to flow backward into the left lower heart chamber (ventricle).
Aortic valve disease may be present at birth (congenital heart disease), or it may occur later in life due to other health conditions.
Treatment for aortic valve disease depends on the type and severity of disease. Some people may need surgery to repair or replace the aortic valve.
Symptoms
Some people with aortic valve disease may not notice symptoms for many years. Signs and symptoms of aortic valve disease may include:
- Whooshing or swishing heart sound (heart murmur)
- Chest pain or tightness
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Fatigue after activity or having less ability to be active
- Irregular heartbeat
- Shortness of breath, particularly during vigorous activity or when lying down
- Not eating enough (mainly in children with aortic valve stenosis)
- Not gaining enough weight (mainly in children with aortic valve stenosis)
When to see a doctor
If you're having sudden chest pain, get emergency medical help.
Make an appointment with a health care provider if you have signs or symptoms of valve disease, such as shortness of breath, fatigue after activity, or sensations of a pounding or an irregular heartbeat. Sometimes the first signs of aortic valve disease are related to heart failure. See a health care provider if you have fatigue that doesn't get better with rest, shortness of breath, and swollen ankles and feet, which are common symptoms of heart failure.
Causes
Chambers and valves of the heart
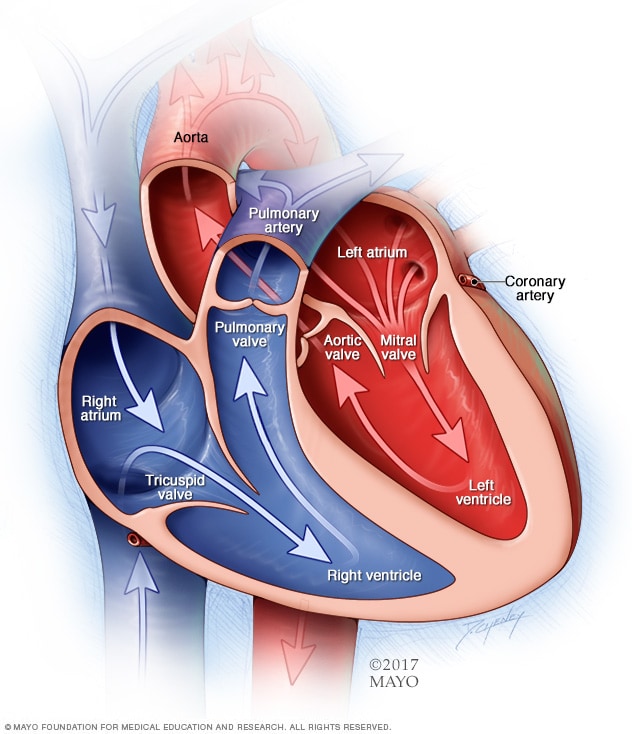
Chambers and valves of the heart
A typical heart has two upper and two lower chambers. The upper chambers, the right and left atria, receive incoming blood. The lower chambers, the more muscular right and left ventricles, pump blood out of the heart. The heart valves, which keep blood flowing in the right direction, are gates at the chamber openings.
Aortic valve disease may be caused by a heart defect present at birth (congenital heart defect). Other causes of aortic valve disease later in life include:
- Age-related changes to the heart
- Infections
- High blood pressure
- Injury to the heart
To better understand the causes of aortic valve disease, it may be helpful to know how the heart valves typically work.
The heart has four valves that keep blood flowing in the correct direction. These valves are:
- Aortic valve
- Mitral valve
- Tricuspid valve
- Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve stenosis
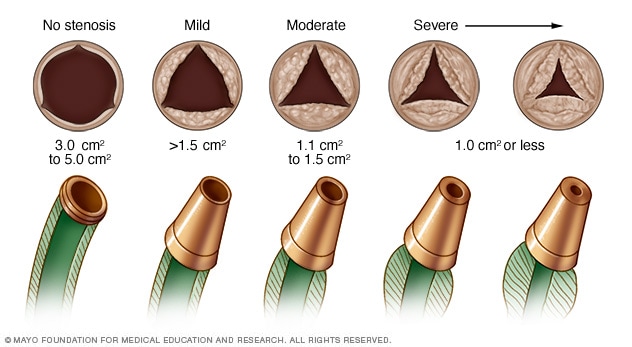
Aortic valve stenosis
In aortic valve stenosis, the aortic valve opening is narrowed (top row). The narrowing requires increased pressure within the heart to pump blood across a smaller opening. Eventually this reduces the heart's ability to pump blood to the body. This is similar to attaching smaller and smaller nozzles to the end of a garden hose (bottom row). The narrowing from the nozzle slows the forward flow of water and results in pressure buildup within the garden hose.
Each valve has flaps (cusps or leaflets) that open and close once during each heartbeat. Sometimes, a valve doesn't open or close properly. This can reduce or block blood flow through the heart to the rest of the body.
In aortic valve disease, the valve between the lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) and the body's main artery (aorta) doesn't work properly. The valve may be thickened and stiff (stenosis) or it may not close properly, causing blood to flow backward.
Risk factors
Many things can raise the risk of aortic valve disease, including:
- Older age. Calcium deposits can build up on the aortic valve as people age, causing the aortic valve to stiffen and become narrow.
- Heart valve problems present at birth (congenital heart defects). Some people are born with a missing, extra or fused valve flap (cusp), increasing the risk of aortic valve regurgitation.
- Rheumatic fever. This complication of strep throat can cause aortic stenosis, a type of valve disease. If you have heart valve disease due to rheumatic fever, it's called rheumatic heart disease. If not, it's called nonrheumatic heart disease.
- Inflammation of the lining of the heart's chambers and valves (endocarditis). This life-threatening condition is usually caused by infection. It can damage the aortic valve.
- History of radiation therapy to the chest. Some types of cancer are treated with radiation therapy. Symptoms of heart valve disease may not be noticed until many years after radiation therapy is received.
- Other health conditions. Chronic kidney disease, lupus and Marfan syndrome, a connective tissue disease, can increase the risk of aortic stenosis or regurgitation.
Complications
Potential complications of aortic valve disease may include:
- Blood clots
- Stroke
- Heart failure
- Heart rhythm problems (heart arrhythmias)
- Death due to sudden cardiac arrest
Proper diagnosis and treatment can help reduce the risk of complications.
Nov. 17, 2021